Visualize optimization results
The default optimization report has a filter enabled on the header row to easily sort and filter different parameter combinations. A surface chart can be helpful to visualize the interaction between two different parameters at a glance. For example, using data from the example in Optimization, we can plot the Sharpe Ratio with respect to the short and long moving average lengths.
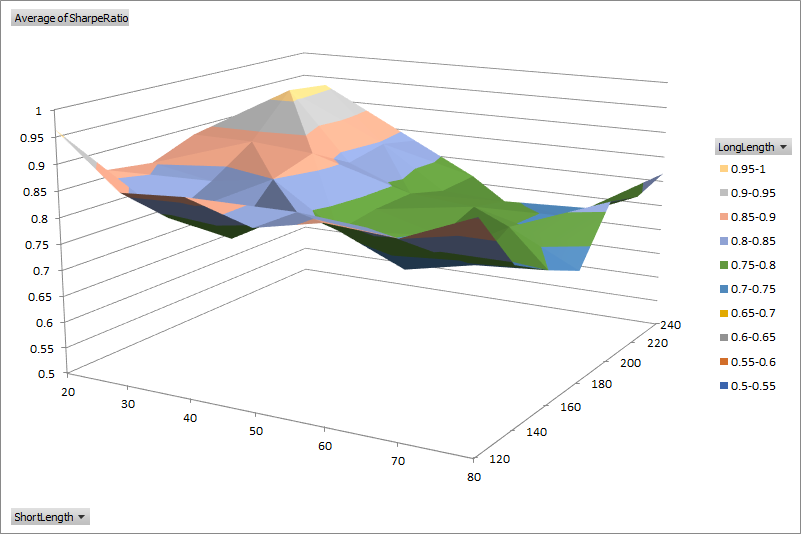
To create surface charts automatically from an optimization report, place the macro below within your Excel Personal Macro Workbook and assign a hotkey.
Public Sub CreateSurfaceChart()
Dim r As Range
Dim ws As Worksheet
Dim pivot As PivotTable
Range("A1").Select
Range(Selection, Selection.End(xlToRight)).Select
Range(Selection, Selection.End(xlDown)).Select
Set r = Selection
Set ws = Sheets.Add
ActiveWorkbook.PivotCaches.Create(SourceType:=xlDatabase, SourceData:= _
r, Version:=xlPivotTableVersion14).CreatePivotTable _
TableDestination:=ws.Name & "!R3C1", TableName:="PivotTable1", DefaultVersion _
:=xlPivotTableVersion14
ws.Select
ws.Cells(3, 1).Select
Set pivot = ws.PivotTables("PivotTable1")
With pivot.PivotFields(1)
.Orientation = xlRowField
.Position = 1
End With
With pivot.PivotFields(2)
.Orientation = xlColumnField
.Position = 1
End With
pivot.AddDataField pivot.PivotFields("Sharpe Ratio"), "Average of SharpeRatio", xlAverage
ws.Shapes.AddChart.Select
ActiveChart.ChartType = xlSurface
Set r = ws.Range(ws.Cells(3, 1), ws.Cells(3, 1).Offset(pivot.RowFields.Count, pivot.ColumnFields.Count))
ActiveChart.SetSourceData Source:=r
ws.Shapes(1).Top = 50
ws.Shapes(1).Left = 50
ws.Shapes(1).Width = 600
ws.Shapes(1).Height = 400
End Sub